TUTORIAL
- SIMPLE SEARCH
- ADVANCED SEARCH
- EXAMPLES
- UPLOAD DATA
- GLOSSARY
SIMPLE SEARCH
SIMPLE SEARCH
Under simple search, users can search by keyword or by Entry ID.
1. SEARCH BY KEYWORD
The user can search by keyword, such as Protein name, PDB ID, PubMed ID, or Experimental Technique, and obtain the results. The following is the search results for the keyword "surface plasmon resonance."
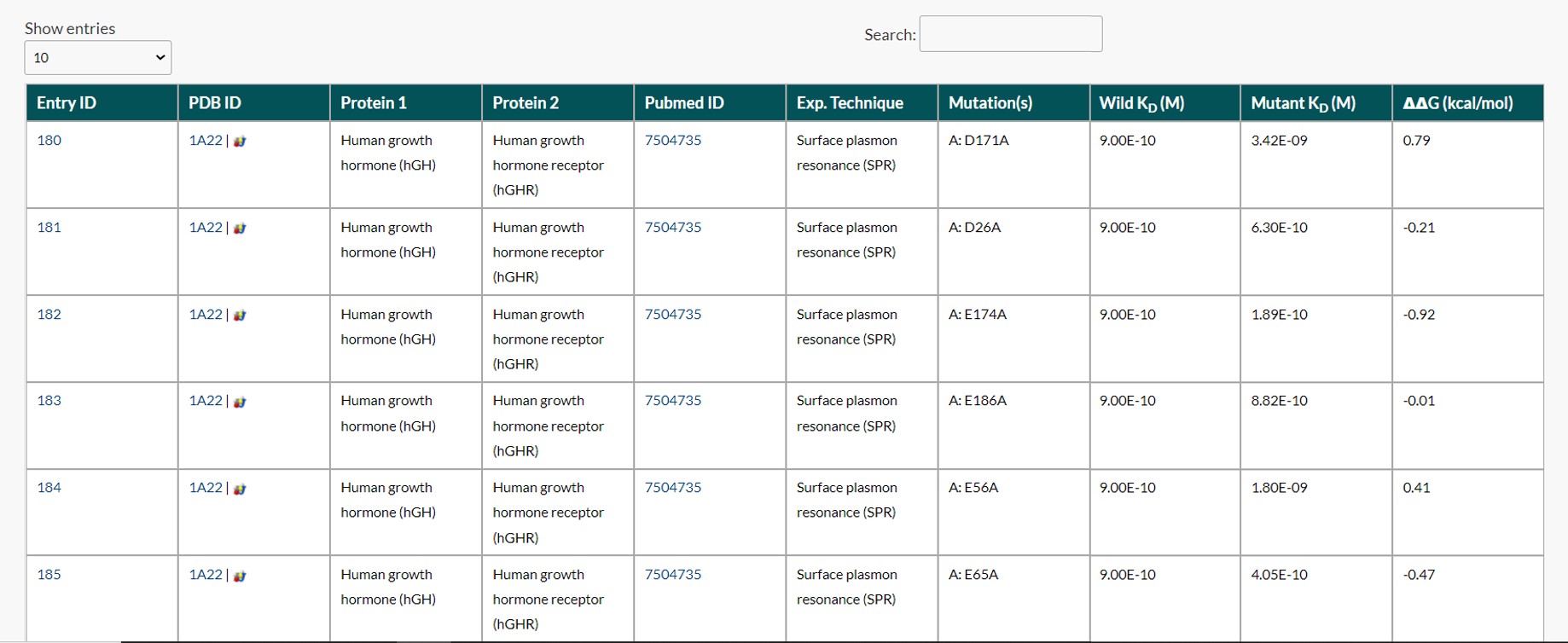
The result page only displays the default columns; however, if users want any other specific column(s), they can use the Advanced Search tab.
Note: Users can only search with a single keyword; multiple keywords are not accepted.
2. SEARCH BY ENTRY ID

Users can search for Entry ID available (any number from 1 to 5376). The image below depicts the search result page for the Entry ID "4091". Users can obtain all available information related to a specific ID.

ADVANCED SEARCH
ADVANCED SEARCH
There are two sections under Advanced Search: a Build Search Query form (to specify a search query) and a Display Options form (to choose the columns to be displayed). All of the fields are optional. Leaving all fields blank, on the other hand, will yield no result. Please enter a query in at least one of the fields in the Build Search Query form. Multiple queries will be processed using AND logic (e.g., if the user specifies a PDB ID "1A22" and pH 5, then the search will retrieve entries for which both conditions are true). The Reset button will refresh the search form, displaying the default options, whereas the Select All button will select all options in the Display Options form.
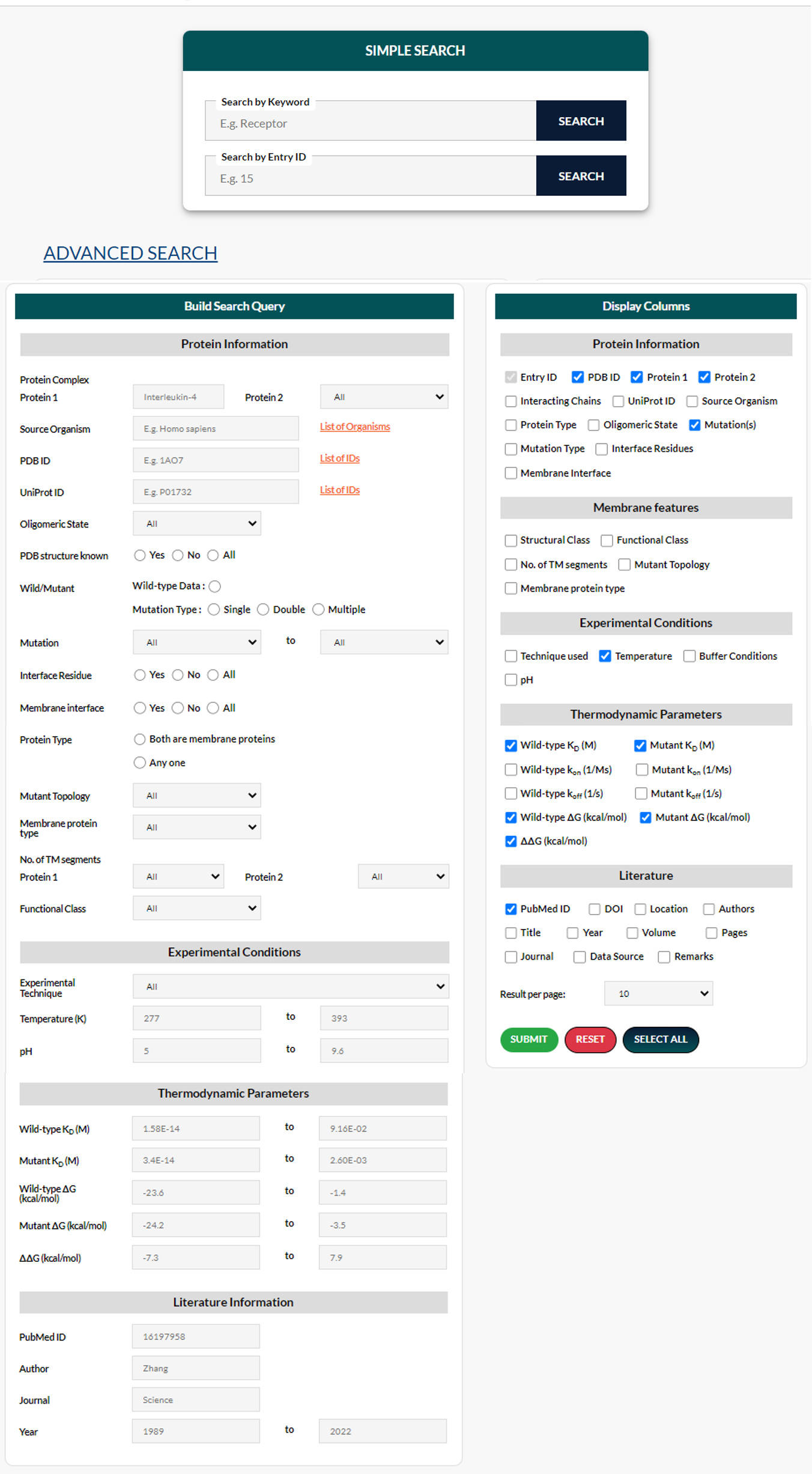
Build Search Query form:
Protein Information: This section allows the user to search for a specific protein or protein complex by name, source organism, PDB ID, UniProt ID, mutation(s), type of mutation, interface residue, and membrane protein-specific features such as protein type, mutant topology, and type of pass.
The protein complex consists of two search fields and can be used to search for a particular protein or a protein complex by name. For example, if the user enters “Interleukin”, they can get suggestions to choose from the Protein 1 drop-down box (as shown in the figure above). If this box is filled (e.g. Human interleukin-2 (hIL-2)), the second box will provide a list of proteins that interact with protein 1 and have known affinity data deposited in MPAD (as shown in the figure below).

Wild-type data search: Users can search for only wild-type data by selecting “Wild-type Data” under the Wild/Mutant option field. Users can get the list of all wild-type data in the database if this option is used without any additional search query.
Mutant data search: If users require mutant data, they can specify the type of mutation - single, double, or multiple by selecting it under the Wild/Mutant option field. Also, for residue mutation, two fields are provided. The first is used to specify the wild-type residue, whereas the second is used to specify the mutant residue. The results may include both single and multiple mutations. All chains are searched for the mutation specified by the user.
Experimental Conditions: Users can search by giving any experimental technique, temperature (K), or pH. For the experimental technique, a drop-down is provided which contains all the techniques available in the database. Please note that due to the diversity of terms that might be used to refer to the same experimental technique, searching by a particular technique may not yield complete results. We have attempted to keep a consistent nomenclature wherever possible. However, in some cases, the technique was not stated, or the description was too vague to determine the exact name for the technique used to obtain the data.
Thermodynamic Parameters: Users can search with various thermodynamic parameters such as Wild-type KD (M), Mutant KD (M), Wild-type ΔG (kcal/mol), Mutant ΔG (kcal/mol), and ΔΔG (kcal/mol). Users can also search for a particular range of values in each of these parameters. The From field must contain the lower limit and the To field must contain the upper limit. If the To field is left blank, the search will include all entries with values greater than or equal to the lower limit. If the From field is left blank, all entries with values less than or equal to the upper limit will be retrieved. To fields are both the same, only entries that exactly match the specified value will be returned.
Literature Information: Users can search with reference details such as PubMed ID, Author, Journal, and Year. Please note that while searching by author name, it is case-insensitive and can match partial queries with the author's name, but it will not match incorrect spellings. For the Year, Two fields are provided, From and To, to specify the lower and upper limit respectively. For the Year, two fields are provided, From and To, to specify the lower and upper limit respectively.
Display Columns form:
The options allow users to decide which columns should be displayed on the search results page. Some columns are selected by default.
The number of results displayed per page can also be customized by the user.
EXAMPLES
EXAMPLES
★ Tutorial 1: How to retrieve only the wild-type data present in MPAD?

★ Tutorial 2: How to retrieve data from MPAD for a specific complex (e.g., Transferrin-Transferrin Receptor Complex)?

★ Tutorial 3: How to get a list of single pass mutations, which are in membrane region and have ΔΔG values > 0 kcal/mol ?

UPLOAD DATA
UPLOAD YOUR DATA
Authors can contribute previously published data on the binding affinity of membrane protein-protein complexes for inclusion in the database through the Upload Data form. In this section, we will walk you through the process of uploading your data.
The upload form for sharing data is shown:
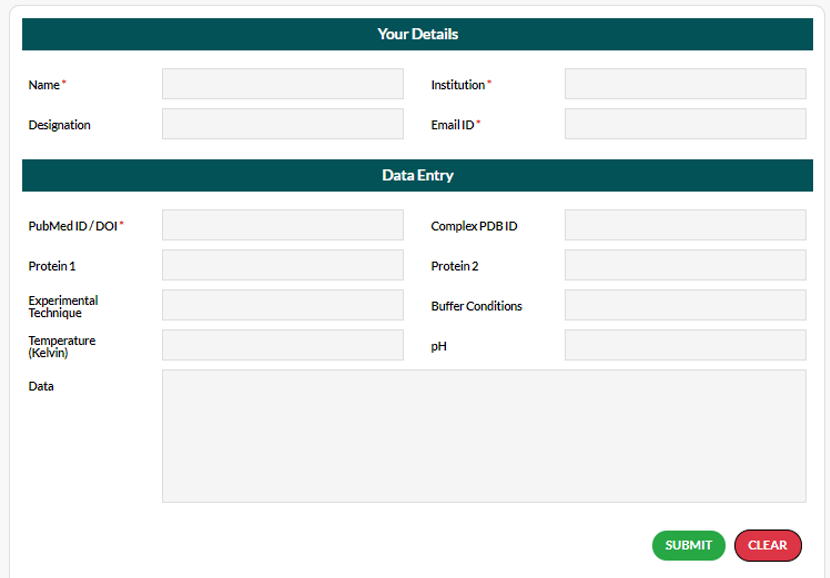
There are two sections in the upload form. The first section is to contact the author if necessary. Please ensure that the contact details are correct. All your personal details will be maintained confidential and will never be shared with third parties.
The second section has data input fields that might finally be included into the database. Therefore, we request the author to ensure accuracy.
For data submission, please follow the guidelines below:
★Please ensure that the data you are sharing has been published and has been indexed with either a PubMed ID or DOI.
★While the PDB ID field is not compulsory (since not all complexes have an experimentally known crystal structure), we strongly recommend providing the PDB ID if available.
★Please provide standard protein names as found in UniProt. It would be helpful if you could include the UniProt accession ID in brackets.
★The experimental technique and buffer conditions can be described as in the database.
★We request that the temperature be provided in Kelvin units.
★The pH field can be filled in with a decimal value ranging from 0.0 to 14.0.
★We have provided a text box for submitters to copy and paste data from spreadsheet or .txt files. Please keep in mind that the mutation must be reported in the format ch:wt-pos-mut or wt-pos-mut if the chain is unknown. If you are submitting KD values, please use scientific notation ('4.3E-09') in Molar (M) units. Please mention the column names in order to identify the type of data (e.g. KD for binding affinity). Please check the FAQ page for the description of the notations and units used and follow accordingly.
★All data submissions are subject to verification and redundancy checks.
Thank you for sharing your data with us.
GLOSSARY
GLOSSARY OF TERMS
| Terms | Explanation |
| ΔG | Binding free energy (kcal/mol); calculated using the formula: ΔG = RT ln(KD) |
| ΔΔG | Difference in binding free energy change between mutant and wild-type complex (kcal/mol); calculated using the formula: ΔΔG = ΔGmut - ΔGwt |
| Entry ID | Each entry of the database is provided with a unique ID. Users can type the Entry ID (any number from 1 to 5340) and obtain the respective ID results. |
| Experimental conditions | It includes experimental details like pH, buffer, temperature and method used used to obtain the thermodynamic data |
| Interface Residue | It refers to the position of the mutation, whether at the interface or not |
| KD | Dissociation rate constant (M) |
| Keyword | It is useful to search by any keyword(s) like protein name, source, PDB ID, UniProt ID, PubMed ID. |
| Koff | Dissociation rate (1/s) |
| Kon | Association rate (1/Ms) |
| Membrane Interface | It refers to if any of the residues of the transmembrane region, is at the interface or not |
| Mutation | Mutation in the protein sequence. Eg. Glu (E) → Lys (K). User can search for mutations by using 2 drop-down boxes available in search page. |
| Mutation Type | Type of mutation namely single, double or multiple mutations |
| No. of TM segments | Transmembrane segment refers to any membrane-spanning protein segment. Depending on the number of transmembrane segments, transmembrane proteins can be classified as single-span or multi-span. |
| Oligomeric State | Refers to the composition of polymeric subunits in quaternary structure. Quaternary structure may be composed either exclusively of identical subunits (homo-oligomers), or composed of different subunits (hetero-oligomers). If the structure is composed of single subunit, then its denoted as “Monomer”. This is based on PDB annotations. |
| PDB ID | Protein Data Bank accession number of complex 3D-structure |
| pH | pH used in the measurement of thermodynamic values |
| Protein type | It refers to whether both proteins of the complex are membrane proteins or any one is a membrane protein while other is a globular protein. |
| PubMed ID | Each entry in linked to a PubMed ID of the article which the reports the specific data |
| T | Temperature used in the measurement of thermodynamic values (K) |
| Topology | Location of the mutation site in the cell membrane |
| Membrane Protein type | Integral and peripheral proteins are two types of proteins that occur in the cell membrane. Integral membrane proteins are permanently attached proteins to the cell membrane while peripheral proteins adhere only temporarily to the biological membrane with which they are associated. Under integral proteins, single-pass membrane proteins cross the membrane only once, while multi-pass membrane proteins span the membrane more than once. |
| UniProt ID | UniProtKB accession number of the protein sequence |
